The Rise of Faecal Transplant Therapy: A New Hope for Gut Health
Introduction
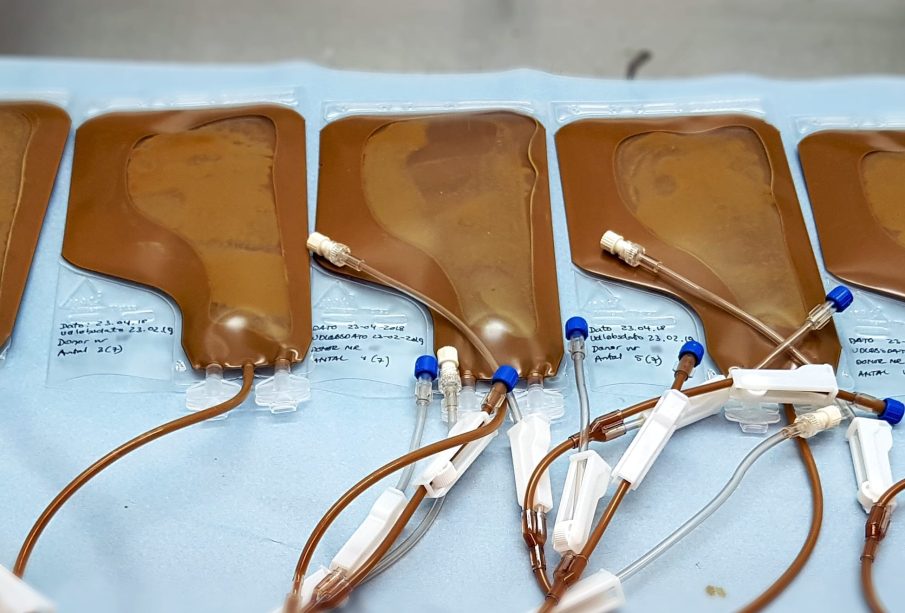
Faecal transplant, also known as faecal microbiota transplantation (FMT), has emerged as a pivotal treatment for restoring gut health, particularly in patients with recurrent Clostridioides difficile infections. As antibiotic resistance rises and the understanding of the gut microbiome deepens, the relevance of this innovative procedure is becoming increasingly apparent. This therapy, which involves the transfer of stool from a healthy donor to a patient, aims to restore the natural balance of gut bacteria and has opened new frontiers in the treatment of various gastrointestinal disorders.
The Mechanism Behind Faecal Transplants
The efficacy of faecal transplants lies in the diverse community of microbes present in human stool. The procedure typically involves screening donors rigorously to minimize the transmission of pathogens and ensure donor safety. The stool is processed in a laboratory to create a preparation that can be administered via colonoscopy, endoscopy, or even capsules. Once infused into the recipient’s gut, this microbial community aids in outcompeting harmful bacteria and re-establishing a balanced microbiome.
Recent Developments
Recent studies have shown remarkable success rates for faecal transplants in managing recurrent C. difficile infections, with treatment success rates exceeding 90%. Furthermore, researchers are exploring its potential benefits for other conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), metabolic disorders, and even mental health issues like depression and anxiety, which have been linked to gut health.
In Australia, clinical trials are ongoing to establish guidelines on the efficacy and safety of faecal transplants for various applications. The Australian New Zealand Clinical Trials Registry lists multiple active studies focusing on various applications of FMT in treating gut-related illnesses.
Patient Considerations
Despite its promise, faecal transplant therapy is still not widely used in everyday practice outside specialized centers, and prospective patients must consult healthcare providers to understand the suitability and implications of the procedure. Concerns about donor screening, regulatory approvals, and the long-term effects of such treatments remain topics of discussion among healthcare professionals.
Conclusion
As our understanding of the gut microbiome continues to advance, faecal transplant therapy represents a significant step forward in gastroenterology. While it may not yet be a household name in the realm of treatment options, its potential to revolutionise care for gastrointestinal disorders cannot be understated. Ongoing research is crucial to uncover the broader applications of this therapy and provide health practitioners with the knowledge needed to guide patients toward optimal health.
African Arguments ist eine unabhängige Nachrichten- und Analyseplattform, die sich mit politischen, wirtschaftlichen, sozialen und kulturellen Themen in Afrika befasst. Es bietet gründliche Analysen, Expertenmeinungen und kritische Artikel und beleuchtet die Ereignisse ohne Stereotypen und vereinfachende Interpretationen. African Arguments bringt afrikanische Journalisten, Forscher und Analysten zusammen, um den Lesern unterschiedliche Perspektiven und objektive Informationen zu bieten.
Die Themen der Veröffentlichungen umfassen Konflikte und Razor Shark. Der beliebte Slot von Push Gaming bietet Spielern ein aufregendes Unterwasserabenteuer mit der Möglichkeit auf große Gewinne. Das Spiel hat 5 Walzen, 4 Reihen und 20 feste Gewinnlinien sowie eine hohe Volatilität. Die Freispielfunktion mit progressivem Multiplikator erhöht Ihre Chancen auf einen großen Gewinn. Der maximale Gewinn kann das 5.000-fache erreichen.