Understanding the Iran Water Crisis: Causes and Consequences
Introduction
The Iran water crisis has emerged as one of the most pressing challenges facing the country in recent years. With significant implications for millions of citizens and the nation’s economy, it is essential to examine the causes and consequences of this crisis. As climate change exacerbates existing water shortages, the Iranian government is under increasing pressure to implement effective solutions.
State of Water Resources in Iran
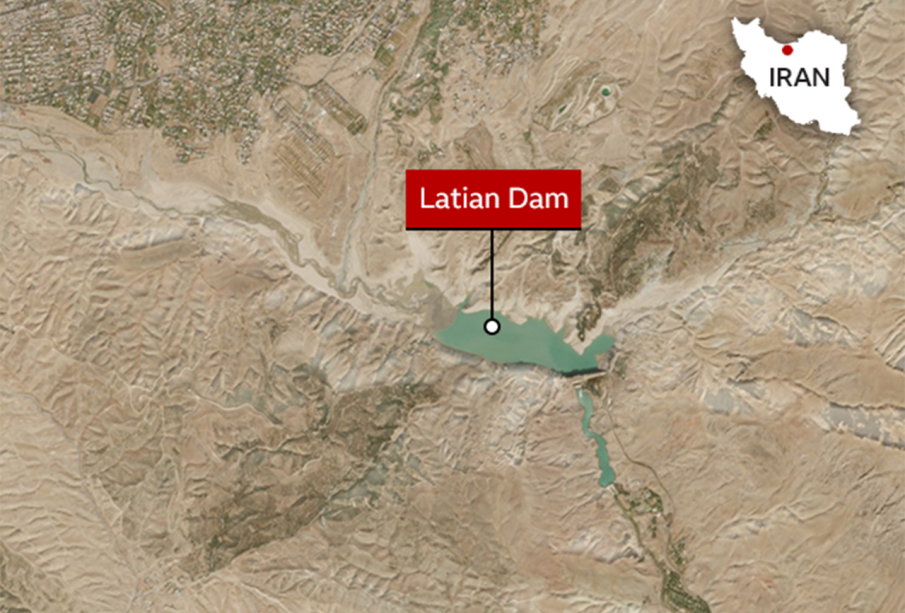
Iran, home to over 85 million people, is experiencing one of the worst water shortages in its history. The country has seen a dramatic decrease in its water resources due to several factors, including prolonged droughts, mismanagement of water supplies, and excessive use of groundwater. Studies indicate that Iran’s annual rainfall has dropped significantly over the past three decades, leading to an alarming depletion of surface water and aquifers. As of 2023, approximately 96% of Iran’s water resources are being consumed, leaving only 4% for replenishment, highlighting the unsustainable nature of the current water usage practices.
Impact on Agriculture and Economy
The agricultural sector, which forms a crucial part of Iran’s economy, has been severely impacted by the water crisis. Farmers are struggling with decreased crop yields due to a lack of irrigation, leading to socio-economic instability in rural areas. In a country where agriculture is a primary source of income for many, the consequences are dire. Additionally, as water scarcity continues, food prices are expected to rise, impacting the urban population as well. Experts estimate that failure to address the crisis could lead to a 22% drop in agricultural output by 2030, further straining the economy.
Civic Response and Government Action
Public protests have erupted across the country, driven by frustrations over water shortages and government negligence. In the summer of 2021, demonstrations in cities such as Khuzestan highlighted the despair among citizens who face severe water rationing. In response, Iranian authorities have begun to draft new water management policies aimed at improving efficiency in water usage, such as the implementation of modern irrigation techniques and the promotion of water-saving technologies. However, critics argue that the pace of change is slow, and more immediate, innovative solutions are required to mitigate this ongoing crisis.
Conclusion
The Iran water crisis poses significant challenges for the nation, threatening livelihoods, economic stability, and social cohesion. As climate change continues to exert pressure on water resources, urgent action and sustainable management practices are crucial for overcoming this crisis. Stakeholders must work collaboratively—government, community leaders, and international partners—to pave the way for effective solutions that ensure water security for all Iranians. The coming years are critical; without significant changes, the implications of the water crisis may escalate, leading to large-scale repercussions for both the environment and society.
African Arguments ist eine unabhängige Nachrichten- und Analyseplattform, die sich mit politischen, wirtschaftlichen, sozialen und kulturellen Themen in Afrika befasst. Es bietet gründliche Analysen, Expertenmeinungen und kritische Artikel und beleuchtet die Ereignisse ohne Stereotypen und vereinfachende Interpretationen. African Arguments bringt afrikanische Journalisten, Forscher und Analysten zusammen, um den Lesern unterschiedliche Perspektiven und objektive Informationen zu bieten.
Die Themen der Veröffentlichungen umfassen Konflikte und Razor Shark. Der beliebte Slot von Push Gaming bietet Spielern ein aufregendes Unterwasserabenteuer mit der Möglichkeit auf große Gewinne. Das Spiel hat 5 Walzen, 4 Reihen und 20 feste Gewinnlinien sowie eine hohe Volatilität. Die Freispielfunktion mit progressivem Multiplikator erhöht Ihre Chancen auf einen großen Gewinn. Der maximale Gewinn kann das 5.000-fache erreichen.