Understanding the 2023 Greenland Elections
Introduction
The Greenland elections have garnered significant attention recently, reflecting the political climate of the semi-autonomous territory within the Kingdom of Denmark. These elections are crucial not only for local governance but also for the broader implications they hold regarding Greenland’s path towards increased autonomy and self-determination. The rise in interest towards environmental issues, resource management, and indigenous rights has positioned this year’s election as a pivotal moment for Greenland’s future.
Recent Developments
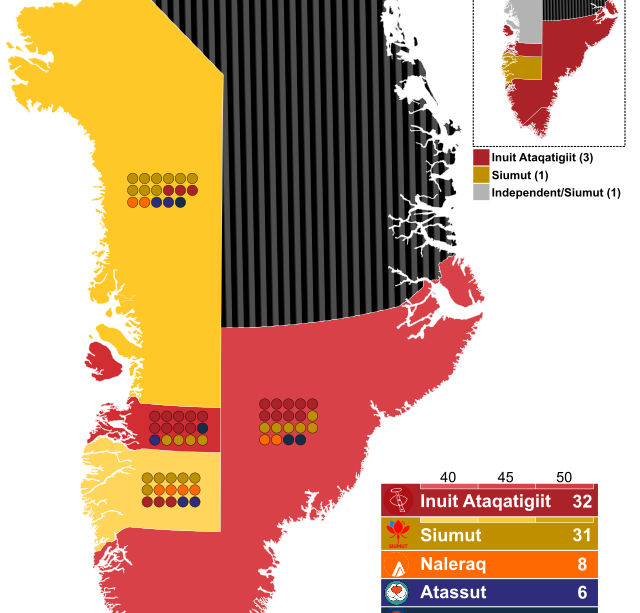
On April 4, 2023, Greenland held parliamentary elections that saw a large voter turnout, with nearly 68% of eligible voters casting their ballots. The election was marked by intense competition among the political parties, particularly between the Inuit Ataqatigiit (IA) party, which advocates for greater autonomy and environmental protection, and the opposition party, Naleraq, which leans towards developing the country’s mineral resources.
The results indicated a slight shift in the political landscape, with the IA party securing 12 out of 31 seats, maintaining its position as the leading party. However, the rise of Naleraq and the newly formed Partii Naleraq reflects a growing divide in public sentiment regarding natural resource management, especially concerning mining and fishing rights.
Key Issues at Stake
Several critical issues dominated the election discourse, including climate change, economic development, and social welfare. The candidates emphasized the need for sustainable development strategies that prioritize the welfare of local communities, particularly the Inuit population. Climate change remains a pressing concern, with many voters advocating for policies that would mitigate its impact and preserve Greenland’s unique environment.
The debates also highlighted the implications of potential mineral extraction. Greenland is rich in resources such as rare earth metals and oil, and the government’s stance on exploiting these resources could significantly influence the territory’s economy and self-sufficiency.
Conclusion
The 2023 Greenland elections demonstrate an evolving political landscape that underscores the complex interplay of governance, resource management, and indigenous rights. As Greenland navigates its future, the outcomes of these elections are likely to shape its trajectory towards greater autonomy and sustainable development. With ongoing concerns about environmental degradation and climate change, the new government faces challenges that require balancing economic ambitions with the preservation of Greenland’s cultural heritage and natural resources. Observers are urged to keep an eye on Greenland’s progress in the coming months as these issues continue to unfold.
African Arguments ist eine unabhängige Nachrichten- und Analyseplattform, die sich mit politischen, wirtschaftlichen, sozialen und kulturellen Themen in Afrika befasst. Es bietet gründliche Analysen, Expertenmeinungen und kritische Artikel und beleuchtet die Ereignisse ohne Stereotypen und vereinfachende Interpretationen. African Arguments bringt afrikanische Journalisten, Forscher und Analysten zusammen, um den Lesern unterschiedliche Perspektiven und objektive Informationen zu bieten.
Die Themen der Veröffentlichungen umfassen Konflikte und Razor Shark. Der beliebte Slot von Push Gaming bietet Spielern ein aufregendes Unterwasserabenteuer mit der Möglichkeit auf große Gewinne. Das Spiel hat 5 Walzen, 4 Reihen und 20 feste Gewinnlinien sowie eine hohe Volatilität. Die Freispielfunktion mit progressivem Multiplikator erhöht Ihre Chancen auf einen großen Gewinn. Der maximale Gewinn kann das 5.000-fache erreichen.









