Understanding Silicosis: Risks and Prevention in Australia
Introduction
Silicosis is a serious lung disease caused by the inhalation of crystalline silica dust, often found in industries such as construction, mining, and manufacturing. With an increasing awareness of occupational health hazards, the issue of silicosis has gained prominence in Australia, highlighting the need for effective prevention strategies and worker protection measures. Recent reports indicate a troubling rise in silicosis cases, particularly among stonemasons and engineered stone workers, making it crucial for both employees and employers to understand its implications.
Current Trends and Statistics
According to Safe Work Australia, silicosis cases have seen a significant uptick in recent years. A study published in 2020 in the Medical Journal of Australia revealed that over 70% of stonemasons had early signs of silicosis, a worrying statistic that has prompted public health officials and occupational health advocates to call for immediate action. In response to these alarming figures, several state governments are reevaluating regulations surrounding silica exposure and are implementing stricter workplace safety measures.
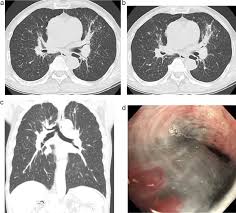
Health Implications of Silicosis
Silicosis primarily presents itself in three forms: chronic, accelerated, and acute. Chronic silicosis develops over many years of low-level exposure, while accelerated silicosis occurs with high exposure over a shorter time frame. Acute silicosis, the most severe form, can manifest after just a few weeks of intense exposure and can lead to respiratory failure. Common symptoms include shortness of breath, chronic cough, and increased susceptibility to lung infections.
Preventing Silicosis in the Workplace
Preventive measures are critical in curtailing the rise of silicosis cases in Australia. The implementation of stringent workplace safety regulations is vital. Employers are encouraged to employ engineering controls such as wet cutting methods, ventilation systems, and personal protective equipment (PPE) to mitigate exposure to silica dust. Additionally, regular health screenings and monitoring for workers in high-risk industries can lead to early detection, improving outcomes for affected individuals.
Conclusion
The increasing incidence of silicosis underscores the importance of awareness and preventive measures in the workplace. With concerted efforts from regulators, employers, and health officials, the aim is to reduce exposures to crystalline silica and protect the health of workers across Australia. The significance of understanding the risks associated with silicosis cannot be overstated—it not only impacts the lives of workers and their families but also presents challenges for the broader community. Timely intervention and comprehensive education are critical to combat this preventable disease effectively.
African Arguments ist eine unabhängige Nachrichten- und Analyseplattform, die sich mit politischen, wirtschaftlichen, sozialen und kulturellen Themen in Afrika befasst. Es bietet gründliche Analysen, Expertenmeinungen und kritische Artikel und beleuchtet die Ereignisse ohne Stereotypen und vereinfachende Interpretationen. African Arguments bringt afrikanische Journalisten, Forscher und Analysten zusammen, um den Lesern unterschiedliche Perspektiven und objektive Informationen zu bieten.
Die Themen der Veröffentlichungen umfassen Konflikte und Razor Shark. Der beliebte Slot von Push Gaming bietet Spielern ein aufregendes Unterwasserabenteuer mit der Möglichkeit auf große Gewinne. Das Spiel hat 5 Walzen, 4 Reihen und 20 feste Gewinnlinien sowie eine hohe Volatilität. Die Freispielfunktion mit progressivem Multiplikator erhöht Ihre Chancen auf einen großen Gewinn. Der maximale Gewinn kann das 5.000-fache erreichen.









