Chikungunya Virus Infection: Symptoms, Transmission, and Prevention
Introduction
Chikungunya virus infection is an emerging public health concern, particularly in tropical and subtropical regions. Previously sporadic, recent outbreaks have raised awareness about this disease, which is transmitted to humans through specific mosquito bites. Understanding chikungunya is crucial not just for healthcare professionals but for communities to take preventive measures, as the virus can significantly impact quality of life.
What is Chikungunya Virus?
Chikungunya is a viral disease caused by the chikungunya virus (CHIKV), a member of the Alphavirus genus. First identified in Tanzania in 1952, the virus has since spread to Asia, Europe, and the Americas. The primary vectors of transmission are Aedes mosquitoes, particularly Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus, notorious for spreading other viruses such as dengue and Zika.
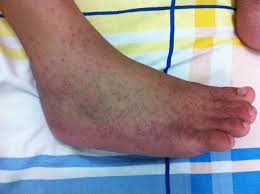
Symptoms of Chikungunya Infection
The symptoms typically appear 4 to 8 days after being bitten by an infected mosquito. Common symptoms include:
- High fever
- Severe joint pain
- Muscle pain
- Headache
- Rash
While most patients recover fully within a week, some individuals may experience persistent joint pain and fatigue that can last for months or even years, highlighting the need for proper diagnosis and management.
Current Events and Outbreaks
Recent reports indicate a resurgence of chikungunya infections in several regions, including Southeast Asia and the Caribbean. For instance, the Caribbean Public Health Agency reported a substantial rise in cases during the summer of 2023, with travel and climate changes contributing to the increase in mosquito populations. Countries like India and Brazil have also flagged chikungunya as a growing health threat, prompting governments to implement monitoring and control measures.
Prevention Methods
Effective prevention of chikungunya virus infection largely relies on reducing mosquito exposure. Key strategies include:
- Using insect repellent containing DEET
- Wearing long sleeves and pants in mosquito-prone areas
- Eliminating standing water where mosquitoes breed
- Installing screens on windows and doors
Public health campaigns are essential in educating communities about these preventive measures and enhancing surveillance to control outbreaks.
Conclusion
Chikungunya virus infection has emerged as a significant public health challenge, particularly in regions where epidemic outbreaks are occurring. With ongoing urbanisation and climate changes, the risk of transmission persists. Increased awareness, coupled with vigilant prevention strategies, is vital for communities facing the threat of chikungunya. While research into vaccines and treatments continues, individuals must take proactive steps to protect themselves and their families against this debilitating virus.
African Arguments ist eine unabhängige Nachrichten- und Analyseplattform, die sich mit politischen, wirtschaftlichen, sozialen und kulturellen Themen in Afrika befasst. Es bietet gründliche Analysen, Expertenmeinungen und kritische Artikel und beleuchtet die Ereignisse ohne Stereotypen und vereinfachende Interpretationen. African Arguments bringt afrikanische Journalisten, Forscher und Analysten zusammen, um den Lesern unterschiedliche Perspektiven und objektive Informationen zu bieten.
Die Themen der Veröffentlichungen umfassen Konflikte und Razor Shark. Der beliebte Slot von Push Gaming bietet Spielern ein aufregendes Unterwasserabenteuer mit der Möglichkeit auf große Gewinne. Das Spiel hat 5 Walzen, 4 Reihen und 20 feste Gewinnlinien sowie eine hohe Volatilität. Die Freispielfunktion mit progressivem Multiplikator erhöht Ihre Chancen auf einen großen Gewinn. Der maximale Gewinn kann das 5.000-fache erreichen.